What Cells Produce Pepsinogen
What Cells Produce Pepsinogen - Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. When pepsinogen is exposed to the stomach's acidic environment,. The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin. Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter. Specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen. Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well as by a number of gastrointestinal hormones.
Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter. Specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen. Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well as by a number of gastrointestinal hormones. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. When pepsinogen is exposed to the stomach's acidic environment,. Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin.
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin. Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. When pepsinogen is exposed to the stomach's acidic environment,. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter. Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. Specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen. Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well as by a number of gastrointestinal hormones.
Solved Which of the following cells secrete Pepsinogen?
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin. Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic.
What Cells Produce Pepsinogen
Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1].
Solved Which of the following cells produce pepsinogen?}ู
Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well as by a number of gastrointestinal hormones. Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin..
SOLVED Question 16 2 pts Correctly match the following chyme produces
Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin. Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter..
Pepsinogen molecule Stock Photo Alamy
Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell).
What Cells Produce Pepsinogen
Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter. Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. Specific cells.
Pepsinogen vs Stomach Unraveling Commonly Confused Terms
Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. When pepsinogen is exposed to the stomach's acidic environment,. Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well.
Answered Which of the following is true of… bartleby
Specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen. Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by. Pepsin is produced by the stomach lining in an inactive form called pepsinogen. The epithelium.
[Solved] If parietal cells stopped secreting HCL, the amount of
Specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen. Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well as by a number of gastrointestinal hormones. Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within.
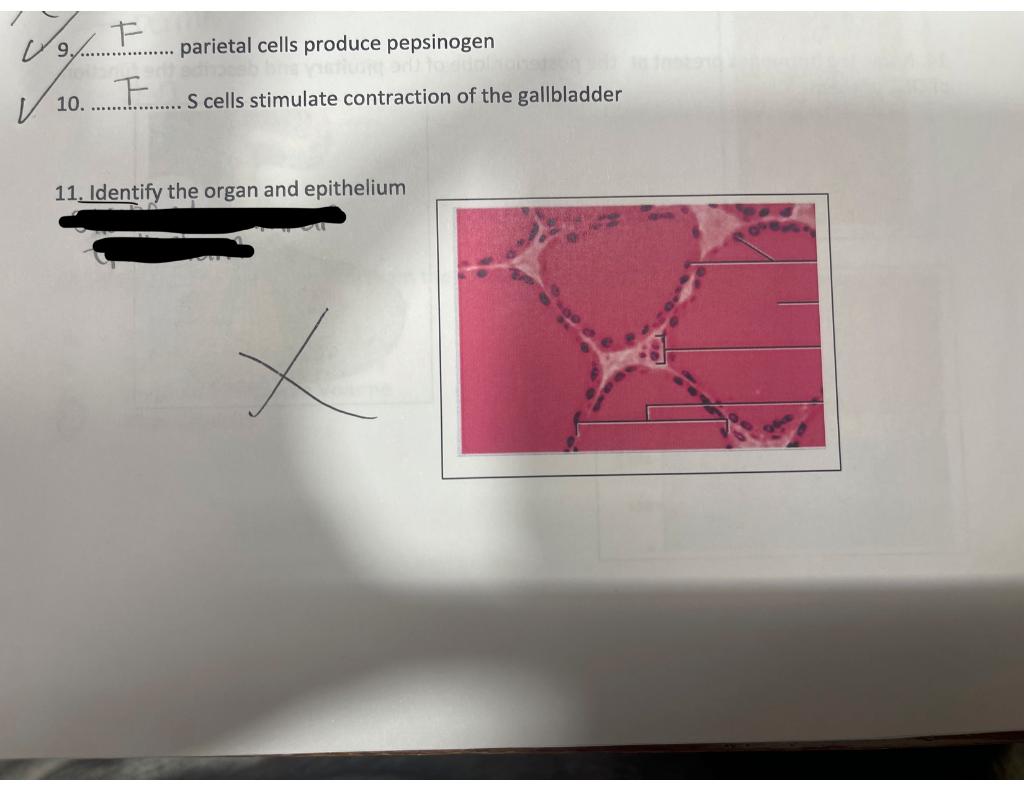
Solved To T parietal cells produce pepsinogen V 10. S cells
Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter. The epithelium of the stomach forms deep pits (fundic or oxyntic glands) where chief cells produce pepsinogen, an inactive precursor of pepsin that. Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach,.
Pepsin Is Produced By The Stomach Lining In An Inactive Form Called Pepsinogen.
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen [1] and chymosin. Pepsinogen, the precursor of pepsin, is released from the chief cell by acetylcholine, as well as by a number of gastrointestinal hormones. When pepsinogen is exposed to the stomach's acidic environment,. Specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen.
The Epithelium Of The Stomach Forms Deep Pits (Fundic Or Oxyntic Glands) Where Chief Cells Produce Pepsinogen, An Inactive Precursor Of Pepsin That.
Pepsin is secreted by chief cells as pepsinogen and acts as an endopeptidase, breaking peptide bonds within the polypeptide and leaving shorter. Pepsinogen is a protein digestive enzyme produced by the gastric chief cells in the stomach, which is converted into the active enzyme pepsin by.