What Does Suboptimal Opacification Of The Pulmonary Arteries Mean
What Does Suboptimal Opacification Of The Pulmonary Arteries Mean - Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the. Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies.
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the. Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies.
Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) with suboptimal
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
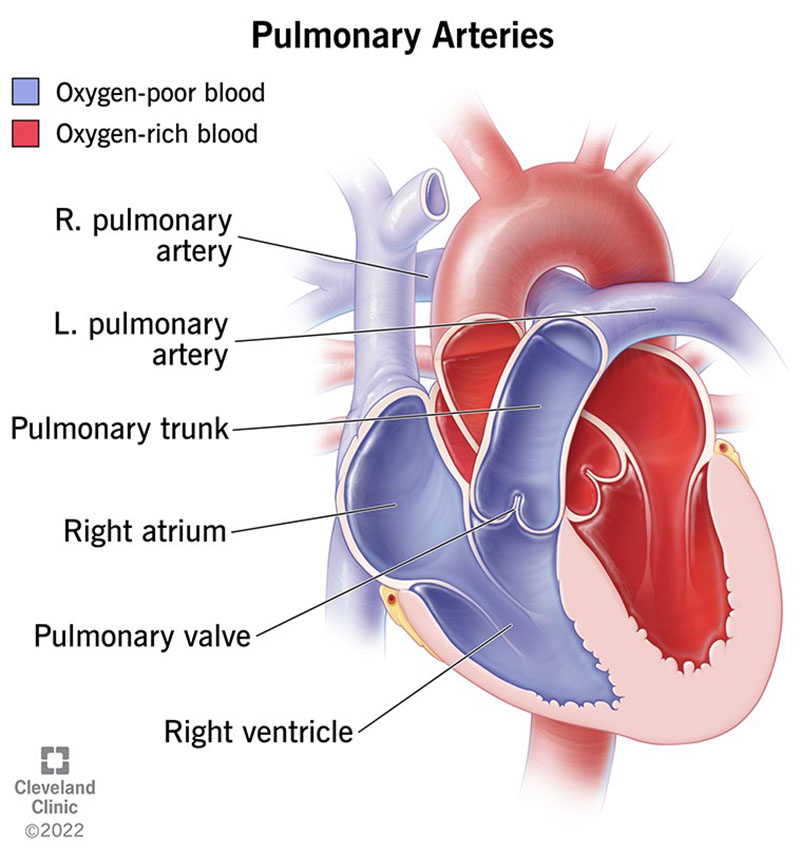
Pulmonary Artery Anatomy, Function, And Significance, 53 OFF
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the. Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies.
Filling defects in bi lateral segmental pulmonary arteriesimage
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the. Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies.
What Does the Pulmonary Artery Pressure Really Tell Us?
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
Pulmonary Arteries Diagram
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
Pulmonary Arteries and Veins TrialQuest Inc.
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the. Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies.
Chest computed tomography. A dilated pulmonary arteries. B
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the. Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies.
CT thorax of pulmonary arteries showed massive right pleural effusion
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
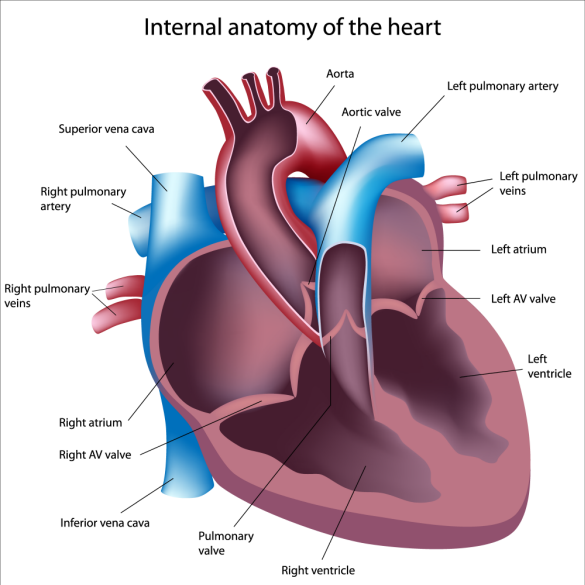
Diagrams Pulmonary Arteries Lungs
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
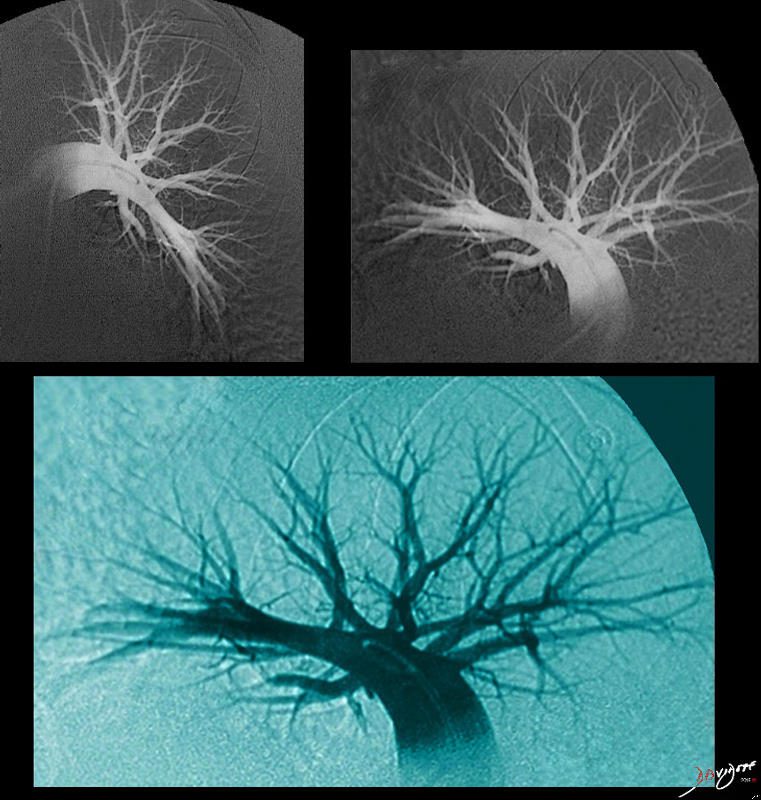
Completion pulmonary angiography shows normal opacification of the
Transient interruption of contrast (tic) is a common flow artifact seen in ct pulmonary angiography (ctpa) studies. Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.
Transient Interruption Of Contrast (Tic) Is A Common Flow Artifact Seen In Ct Pulmonary Angiography (Ctpa) Studies.
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the.