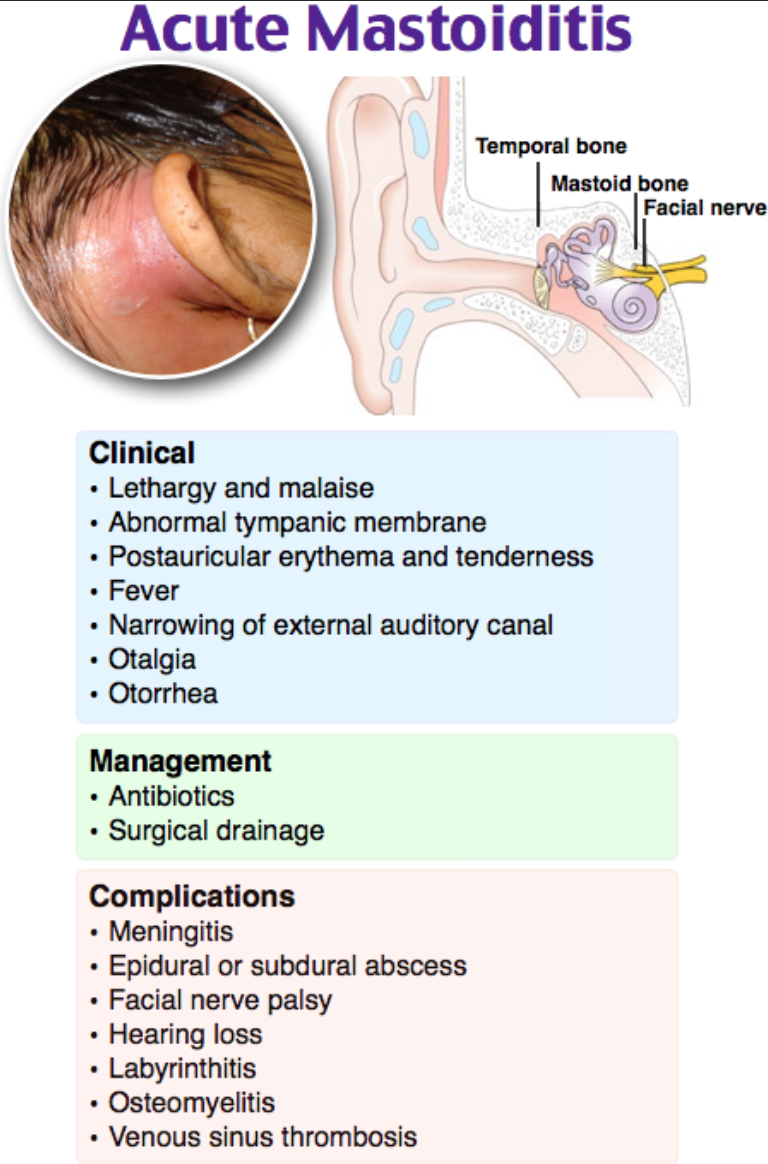
What Is Bilateral Mastoid Effusions
What Is Bilateral Mastoid Effusions - Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis.
Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis. Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain.
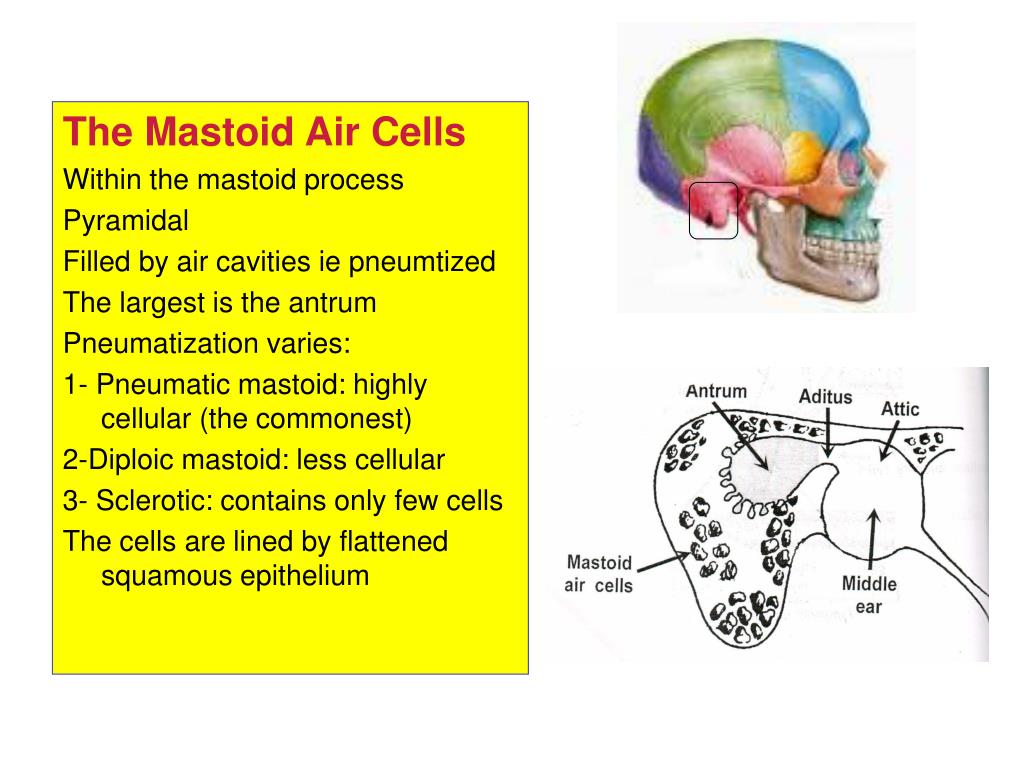
Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis.
Emergency Medicine EducationEM3AM Mastoiditis emDOCs
Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous.
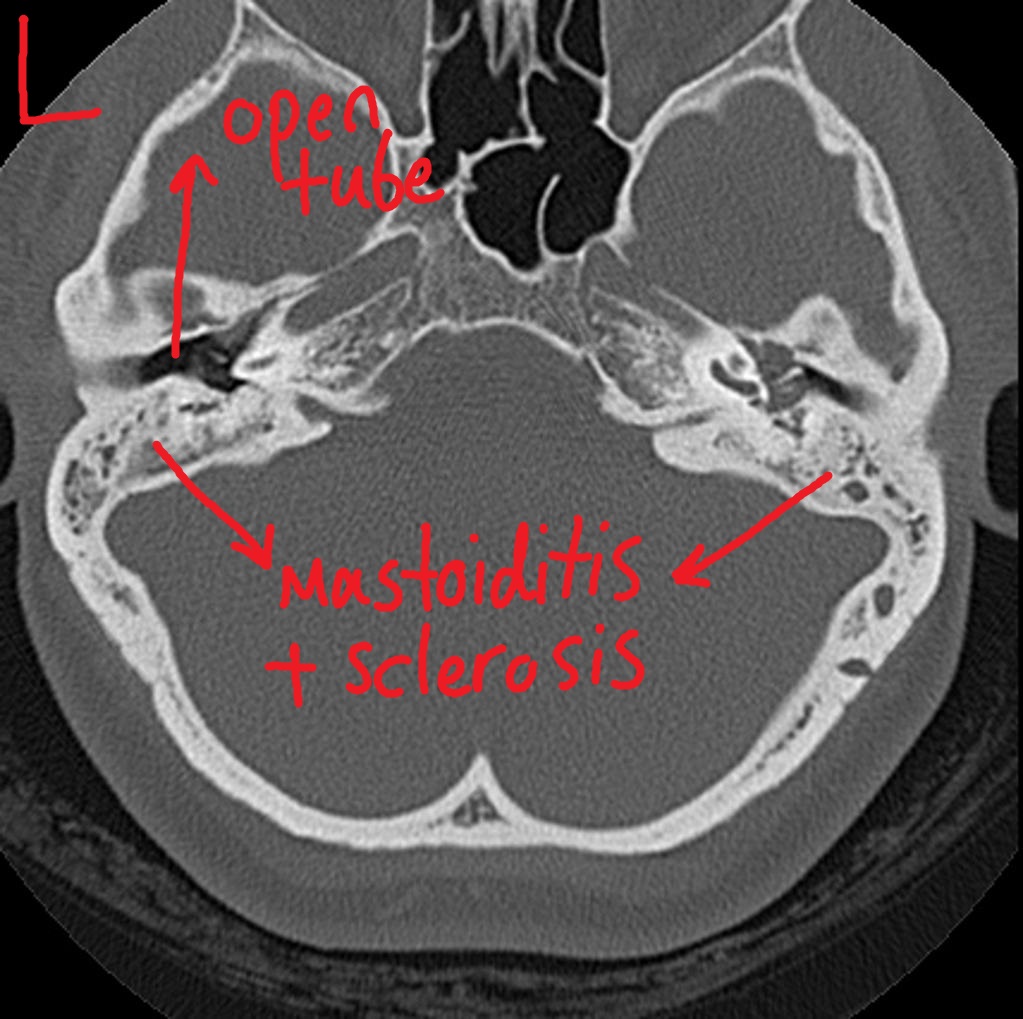
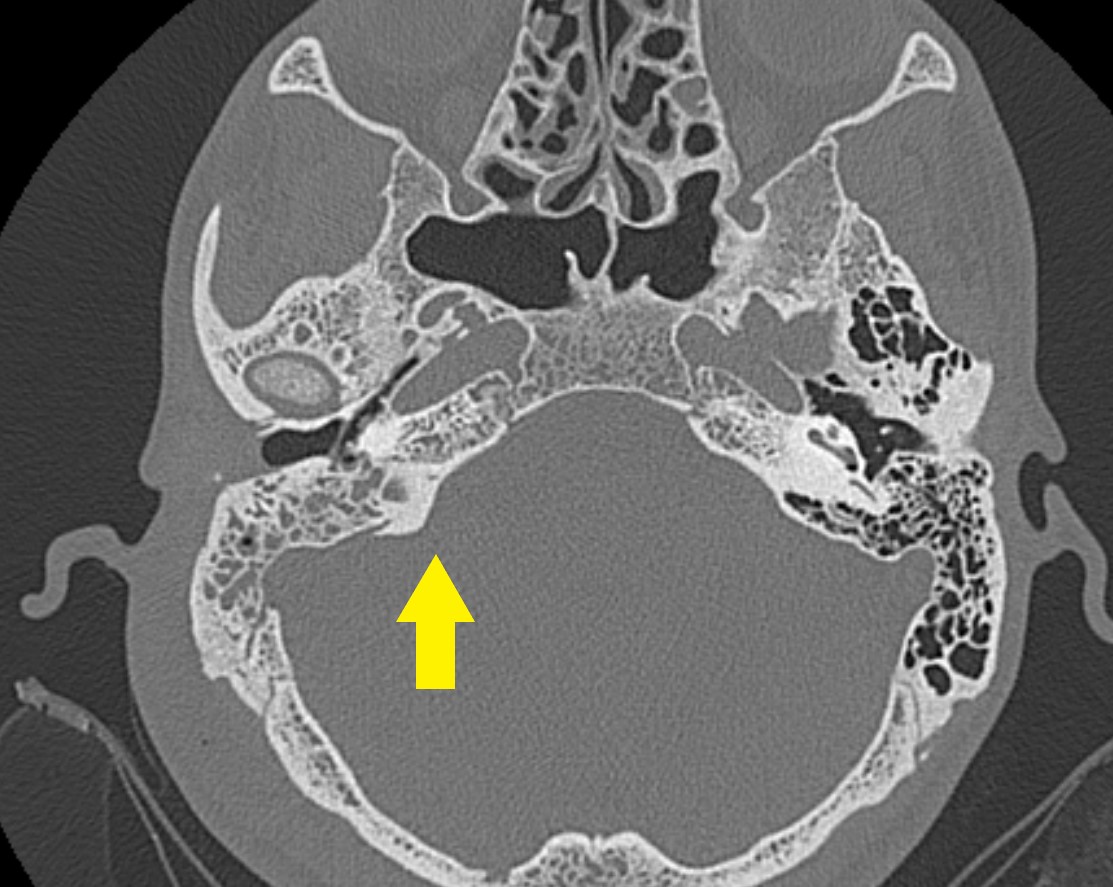
MR imaging of the cranium with bilateral mastoiditis (blue arrow) and
Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which.
Computed tomography scan showing bilateral mastoiditis Download
Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Because the mastoid air cells are.
Mastoiditis CT wikidoc
Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is. Because the mastoid air cells are.
Mastoid Process Location, Function and Pictures
Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. Because the mastoid air cells are.
Mastoid Bone Fracture
Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or.
Ear Anatomy Mastoid
If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in.
(PDF) Bilateral mastoid emissary vein enlargement causing occipital
Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. In.
Mastoiditis CT wikidoc
If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will.
Figure 2 from Radiographic Mastoid and Middle Ear Effusions in
Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during. In only a small number of patients, this relates to inflammatory disease of. Fluid signal in the mastoid can be such an incidental finding on mri of the brain. Middle ear infections cause most.
In Only A Small Number Of Patients, This Relates To Inflammatory Disease Of.
Mastoiditis is an infection of your mastoid process, or the large bone behind your ear. If you or your child is diagnosed with acute. Middle ear infections cause most cases of mastoiditis. Because the mastoid air cells are contiguous with the middle ear via the aditus to the mastoid antrum, fluid will enter the mastoid air cells during.
Fluid Signal In The Mastoid Can Be Such An Incidental Finding On Mri Of The Brain.
Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for both acute and chronic mastoiditis. Now mastoid effusion basically means that there is collecetion of fluid behind the ear, this is in the bony prominence behind the ear which is.